Description
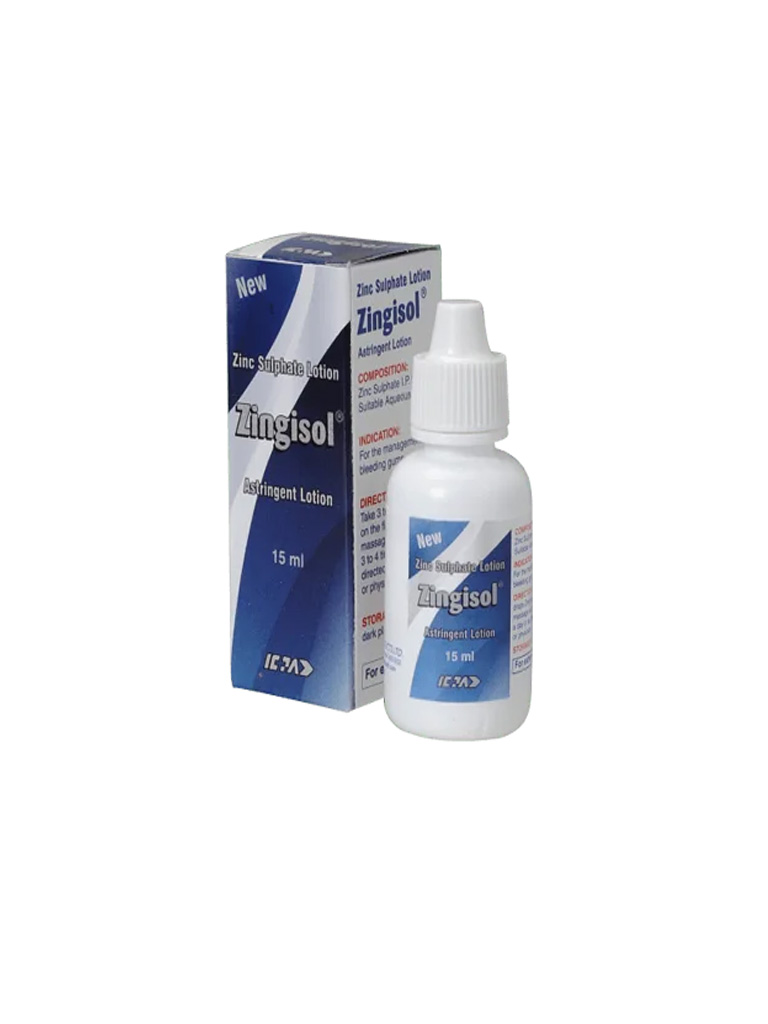
What is Zingisol® Oral Astringent & Haemostatic Lotion?
Zingisol® Oral Astringent & Haemostatic Lotion is used to control plaque formation and inhibit calculus deposition. Zinc salts inhibit volatile sulfur compound production thus helping to reduce halitosis. Its elevated concentration can be maintained in plaque and saliva for a long period, prolonging its beneficial effects. Zinc deficiency has been associated with decreased taste and lingual trigeminal nerve sensitivities as well as reduced salivary flow.
Zinc sulfate is used to treat and prevent zinc deficiency. Before using zinc sulfate, talk to your doctor, pharmacist, or another healthcare provider. You may not be able to use zinc sulfate if you have certain medical conditions. Take 3 to 4 drops of Zingisol on the fingertip and massage each quadrant 3 to 4 times a day, or as directed by the dentist or physician.
Zinc is an essential trace element for maintaining oral health. Due to its effectiveness in oral care, it is a component of many dental materials, mouth rinses, and toothpaste. Zinc is effective in the treatment of oral mucosa diseases especially aphthous ulcers and is useful in the prevention and treatment of plaque-related diseases such as periodontal diseases and dental caries. It has also been identified as a biomarker of oral squamous cell carcinoma and should be evaluated in oral suspicious lesions.
Zinc deficiency is widespread and can be caused by several factors. It is associated with the pathogenesis of common oral mucosa diseases as well as other diseases. Healthy nutrition rich in zinc and other micronutrients is therefore essential in optimizing good oral health. The development of specific recommendations for zinc supplementation and other micronutrients is also important to recognize the role of these micronutrients in maintaining good health.
With common knowledge of the role of zinc in human health and widespread zinc deficiency, education on the sources of zinc and the importance of consuming a diet rich in zinc is vital. Zinc supplements should be given to high-risk groups such as pregnant women, children, adolescents, and the elderly, especially in developing countries. Iron supplements, which can negatively affect zinc absorption, should be taken between meals so that they do not compete with zinc for absorption. Finally, an adequate balance of vitamins and micronutrients, including zinc is important for maintaining oral health and general health.